有了上一篇 angr入门 的铺垫后,现在学习一下 angr 如何给指定内存地址赋值。
Part 4 angr symbolic memory
这次以一个例题来学习如何在 angr 中设置指定地址的值。用 IDA 打开 05_angr_symbolic_memory 文件,查看函数逻辑。依然是使用 scanf 函数读取输入,输入的内容放入了全局变量的四个地址中,可以观察到这个地址并非常规的 bss 段地址,而是一个自定义的内存地址,随后使用 complex_function 对输入的内容进行处理,最后需要和给出的字符串相同:
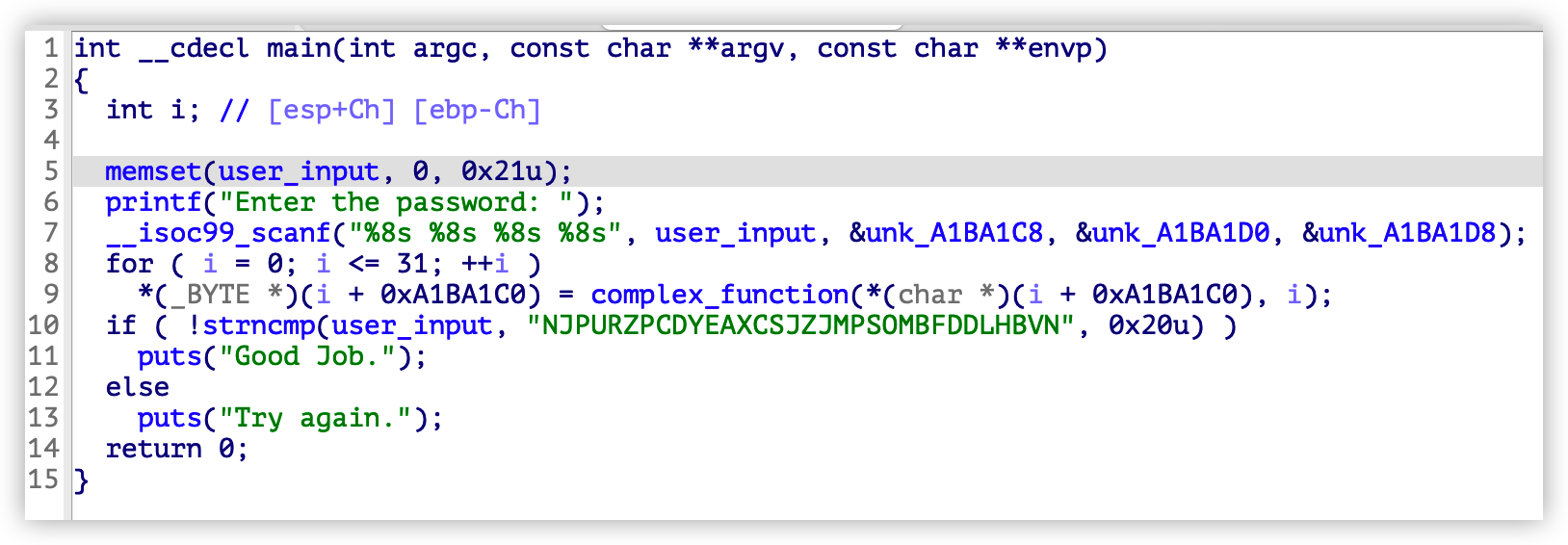
根据之前学习过的 angr 使用方法,可以在 scanf 函数之后符号执行,但是这里有了四个指定的内存地址,需要使用它们进行求解。查看 scaffold05.py 内容如下:
import angr
import claripy
import sys
def main(argv):
path_to_binary = argv[1]
project = angr.Project(path_to_binary)
start_address = ???
initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address)
password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', ???)
password0_address = ???
initial_state.memory.store(password0_address, password0)
simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
def is_successful(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
return ???
def should_abort(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
return ???
simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
if simulation.found:
solution_state = simulation.found[0]
solution0 = solution_state.se.eval(password0,cast_to=str)
...
solution = ???
print(solution)
else:
raise Exception('Could not find the solution')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv)相同代码部分就不详细赘述了,有不清楚的地方可以参考前面angr入门 。主要看看 initial_state.memory.store(password0_address, password0) ,可以把向量值 password0 存储到指定的地址 password0_address 中。我们现在已知的四个地址为 0x0A1BA1C0、0x0A1BA1C8、0x0A1BA1D0、0x0A1BA1D8 ,那么就需要创建四个向量值以此传入。最后直接看修改后的代码:
import angr
import claripy
import sys
def main(argv):
path_to_binary = "./05_angr_symbolic_memory"
project = angr.Project(path_to_binary)
start_address = 0x08048601
initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address)
password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', 64)
password1 = claripy.BVS('password1', 64)
password2 = claripy.BVS('password2', 64)
password3 = claripy.BVS('password3', 64)
password0_address = 0x0A1BA1C0
password1_address = 0x0A1BA1C8
password2_address = 0x0A1BA1d0
password3_address = 0x0A1BA1d8
initial_state.memory.store(password0_address, password0)
initial_state.memory.store(password1_address, password1)
initial_state.memory.store(password2_address, password2)
initial_state.memory.store(password3_address, password3)
simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
def is_successful(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
if b'Good Job.' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
def should_abort(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
if b'Try again.' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
if simulation.found:
solution_state = simulation.found[0]
solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval(password0,cast_to=bytes)
solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval(password1,cast_to=bytes)
solution2 = solution_state.solver.eval(password2,cast_to=bytes)
solution3 = solution_state.solver.eval(password3,cast_to=bytes)
solution = solution0 + b" " + solution1 + b" "+ solution2 + b" "+solution3
print(solution)
else:
raise Exception('Could not find the solution')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv)
代码解读:
start_address选择 0x08048601 是因为这里是scanf函数结束的位置,并且是一个for循环的开始位置,它循环了31次: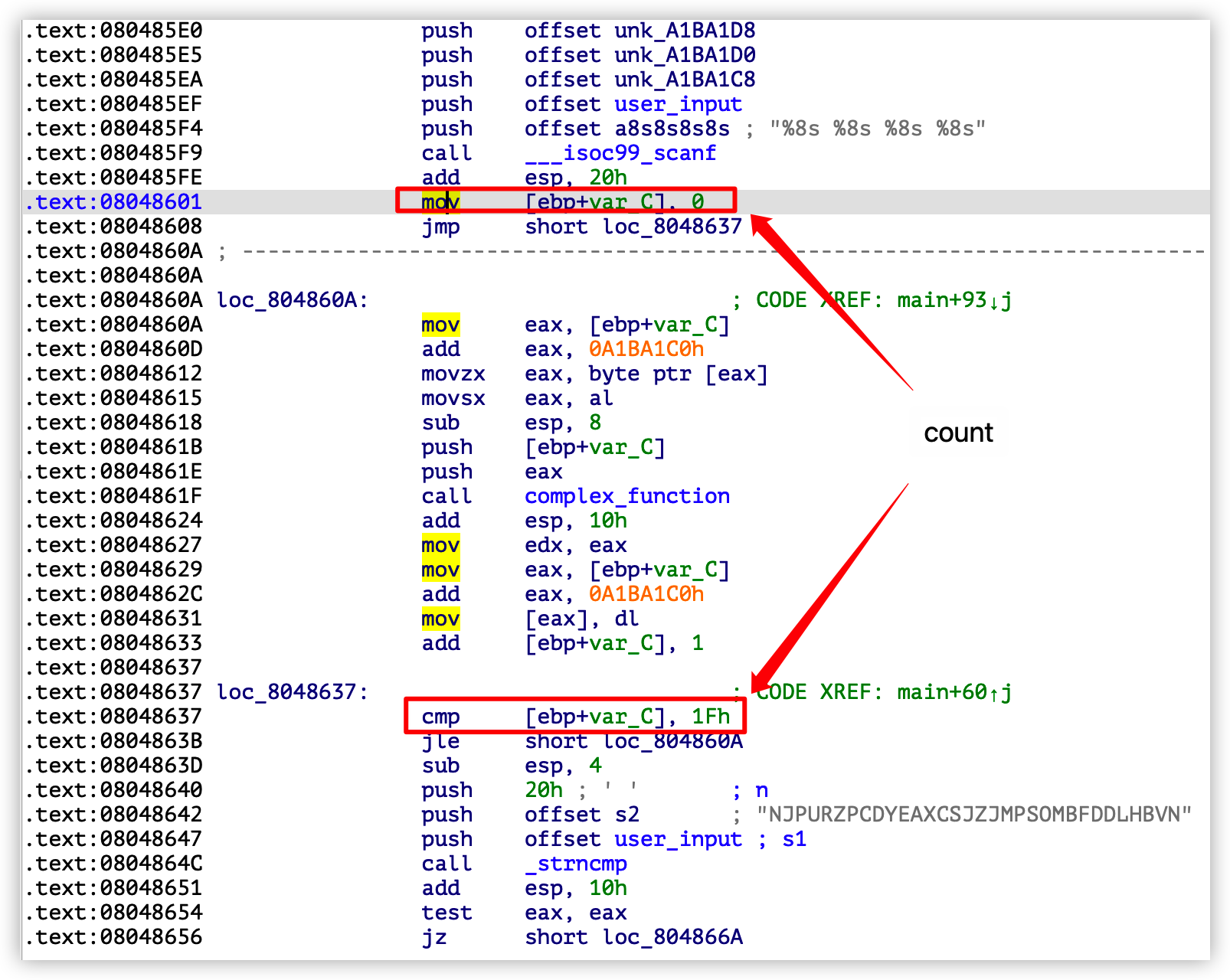
claripy.BVS('password', 64),因为每个地址存储 8 字节,那么就是 64 位solution_state.solver.eval(password,cast_to=bytes)是一个格式化内容的作用,将向量转为bytes类型
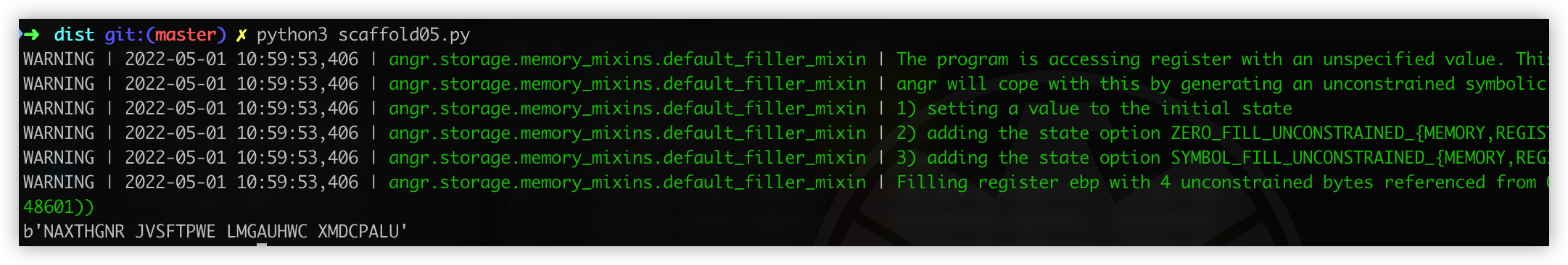
最后得到结果:
Part 5 angr symbolic dynamic memory
其实这一部分和 Part 4 原理差不多,只是将输入内容存储到了分配的堆块内容中,这部分来看看如何应对这种随机地址的问题。
使用 IDA 查看程序逻辑,依然是用 scanf 获取输入,存储到 malloc 函数返回的地址中,buffer0 和 buffer1 都是 bss 段地址,随后对输入进行处理,最后分别对比两个地址内容,成功输出”Good Job”,失败输出”Try again”:
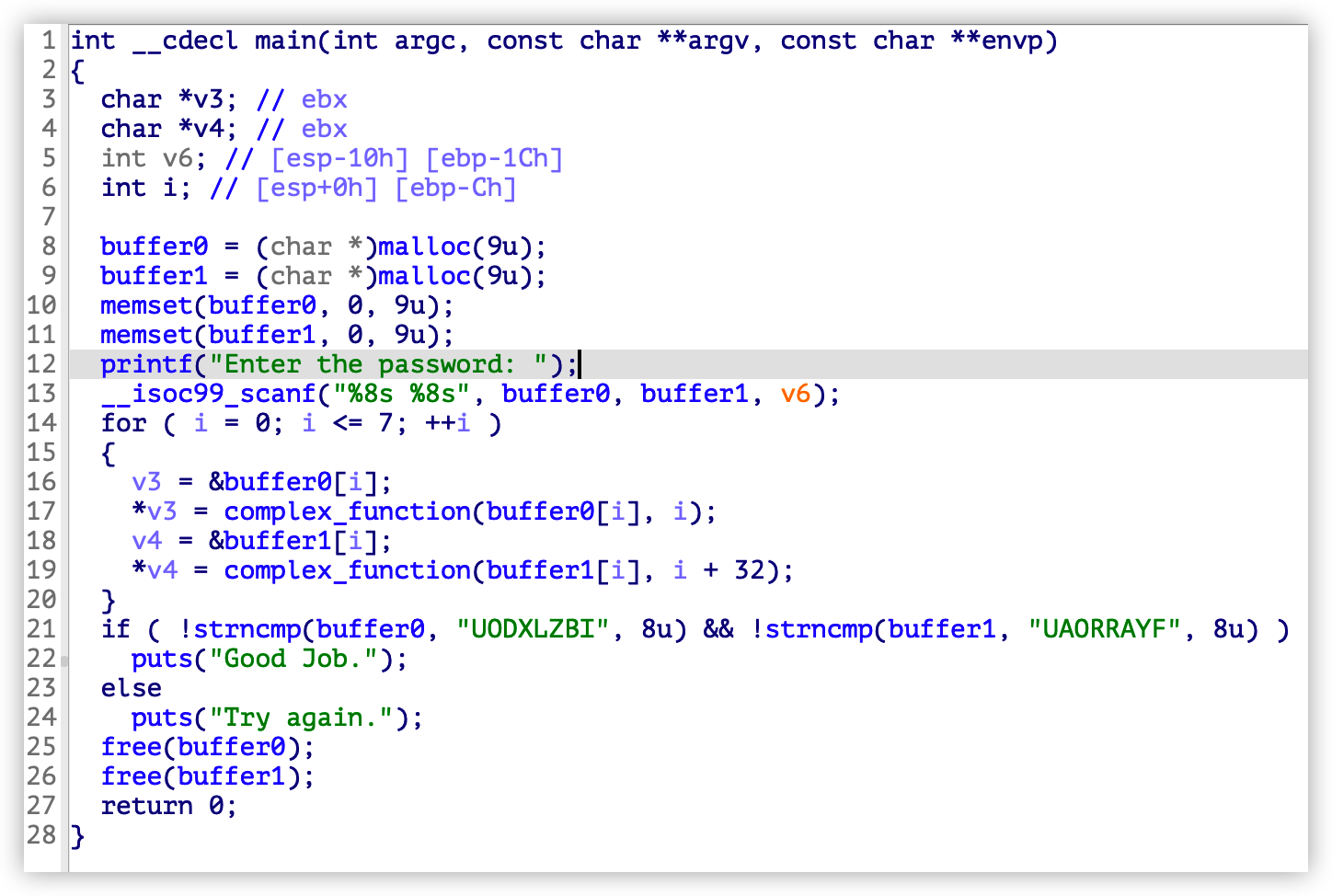
其实 angr 并没有真正的执行程序,所以说在符号执行 malloc 的时候并不是真正的分配了一个堆块,我们只需要分别随意写一个地址到 buffer0 和 buffer1 全局变量中即可。接下来查看完整代码:
import angr
import claripy
import sys
def main(argv):
path_to_binary = "./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory"
project = angr.Project(path_to_binary)
start_address = 0x08048699
initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address)
password0 = claripy.BVS('password0', 64)
password1 = claripy.BVS('password1', 64)
fake_heap_address0 = 0x12345678
pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0 = 0x0ABCC8A4
fake_heap_address1 = 0x12345680
pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1 = 0x0ABCC8AC
initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0, fake_heap_address0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)
initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1, fake_heap_address1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)
initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address0, password0)
initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address1, password1)
simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
def is_successful(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
if b'Good Job.' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
def should_abort(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
if b'Try again.' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
if simulation.found:
solution_state = simulation.found[0]
solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval(password0,cast_to=bytes)
solution1 = solution_state.solver.eval(password1,cast_to=bytes)
solution = solution0 + b' ' + solution1
print(solution)
else:
raise Exception('Could not find the solution')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv)
代码解读:
start_address依然是scanf函数结尾,并且是循环开始的地址
claripy.BVS('password', 64)输入的也是 8 字节,所以是 64 位接下来这段代码,分别将伪造的堆地址 0x12345678、 0x12345680 写入到全局变量
buffer0、buffer1中:
fake_heap_address0 = 0x12345678
pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0 = 0x0ABCC8A4
fake_heap_address1 = 0x12345680
pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1 = 0x0ABCC8AC
initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0, fake_heap_address0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)
initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1, fake_heap_address1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)
initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address0, password0)
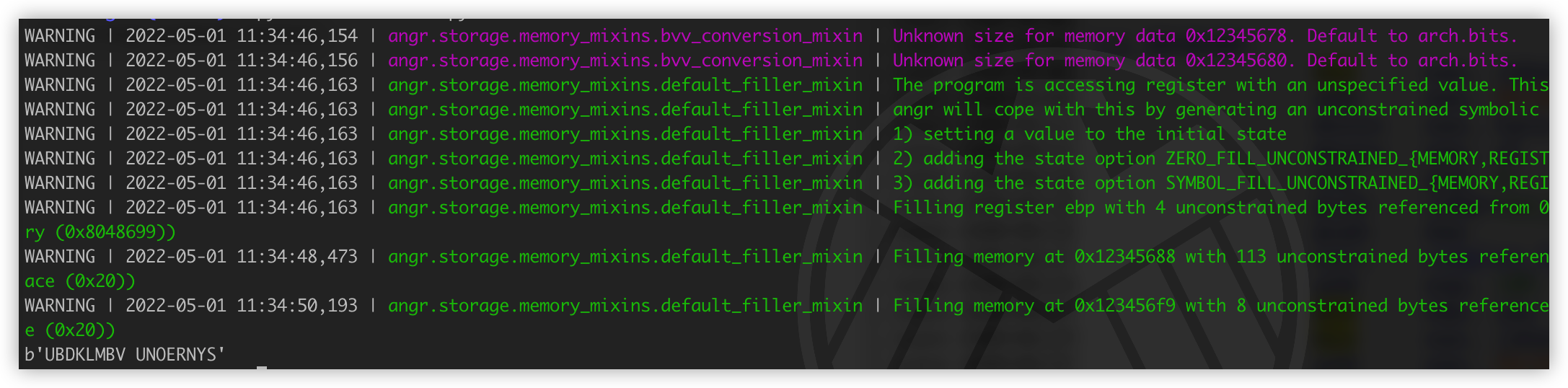
initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address1, password1)把伪造地址给了 buffer0 和 buffer1 之后,处理起来就和 Part4 的过程一样了。最后求解得到结果:
Part 6 angr symbolic file
07_angr_symbolic_file 例子可以用于学习如何模拟一个文件系统,当然还可以用之前学习过的方式解决问题。IDA 分析文件,使用 fread 函数从文件中读取内容,处理后进行对比,如果正确输出”Good Job”,ignore_me 将输入内容写入到文件中,是需要绕过的函数:
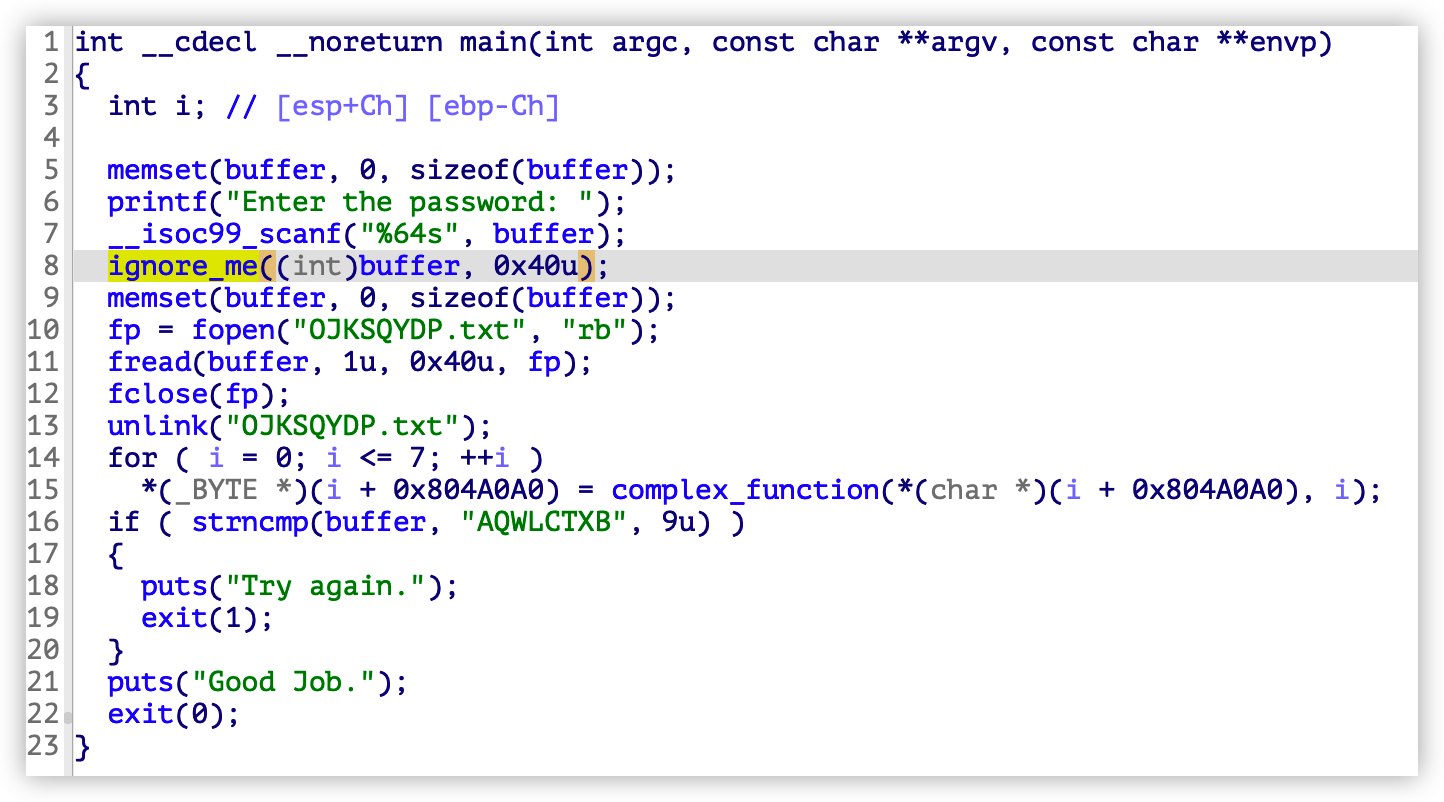
现在要处理的问题:
- 确定
fread读取的文件 - 使用 angr 模拟一个文件系统,替换
fread读取的文件为我们自己的文件 - 用符号值初始化文件,用
fread读取并传播求解,最后得到正确密码
首先确定 start_address 。通过分析,程序从 0x080488EA 开始打开 OJKSQYDP.txt 文件:
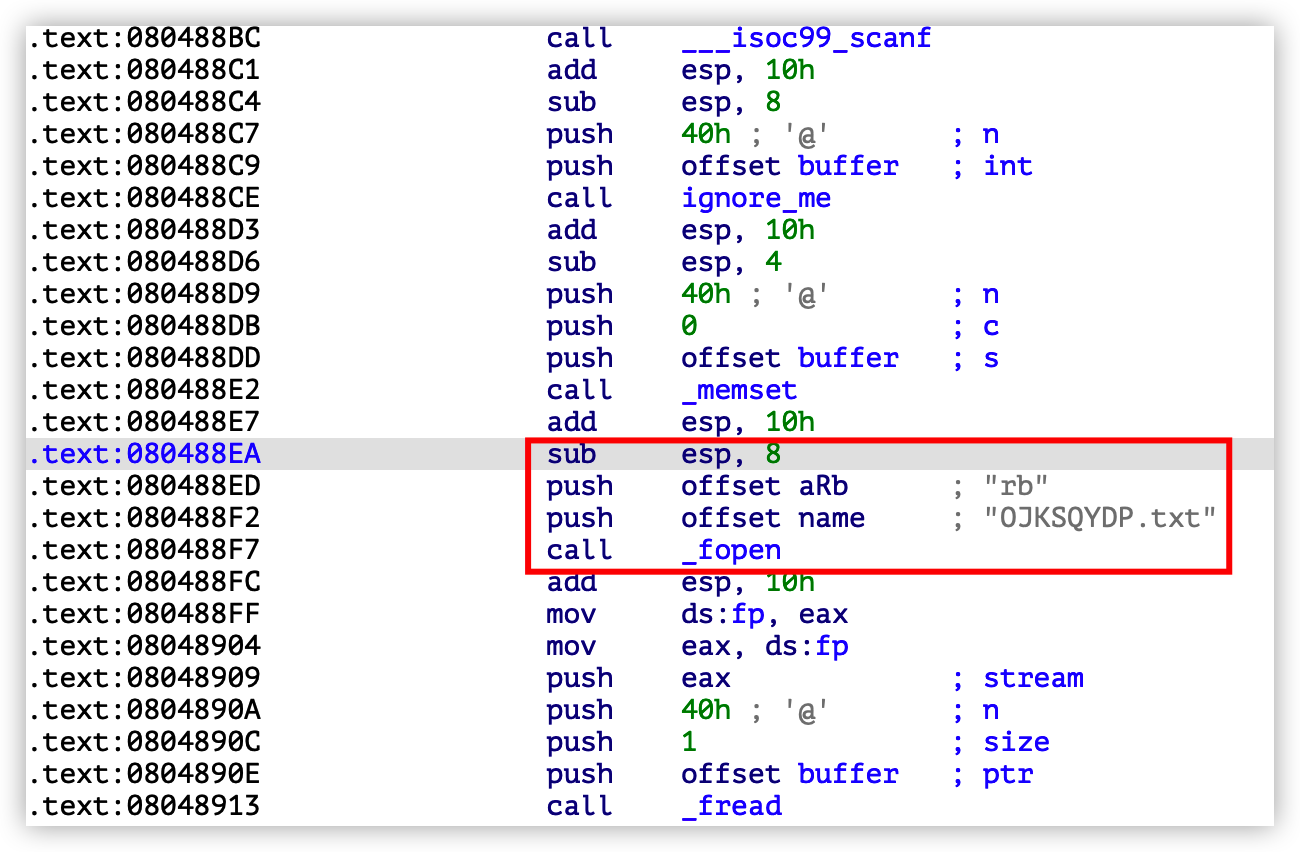
然后指定模拟文件所需的信息,程序中打开的文件名称是固定的,可以用符号替换文件名。由 %64s 可以得知写入的文件大小为 64 字节,但实际只循环读取了 8 字节,在创建向量的时候就是 64 位。然后使用 angr 的 SimFile 模块模拟文件系统:
filename = 'OJKSQYDP.txt'
symbolic_file_size_bytes = 64
password = claripy.BVS('password', symbolic_file_size_bytes)
password_file = angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=password,size=symbolic_file_size_bytes)
initial_state.fs.insert(filename,password_file)之后就是指定 find 和 avoid。完整代码如下:
import angr
import claripy
import sys
def main(argv):
path_to_binary = './07_angr_symbolic_file'
project = angr.Project(path_to_binary)
start_address = 0x080488D6
initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address)
filename = 'OJKSQYDP.txt' # :string
symbolic_file_size_bytes = 64
password = claripy.BVS('password', symbolic_file_size_bytes)
password_file = angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=password,size=symbolic_file_size_bytes)
initial_state.fs.insert(filename,password_file)
simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
def is_successful(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
return 'Good Job.'.encode() in stdout_output
def should_abort(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno())
return 'Try again.'.encode() in stdout_output
simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
if simulation.found:
solution_state = simulation.found[0]
solution = solution_state.solver.eval(password,cast_to=bytes).decode()
print(solution)
else:
raise Exception('Could not find the solution')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv)
最后求得密码: